Nacos配置中心
Nacos除了可以做注册中心,同样可以做配置管理来使用。
当微服务部署的实例越来越多,达到数十、数百时,逐个修改微服务配置就会让人抓狂,而且很容易出错。我们需要一种统一配置管理方案,可以集中管理所有实例的配置。
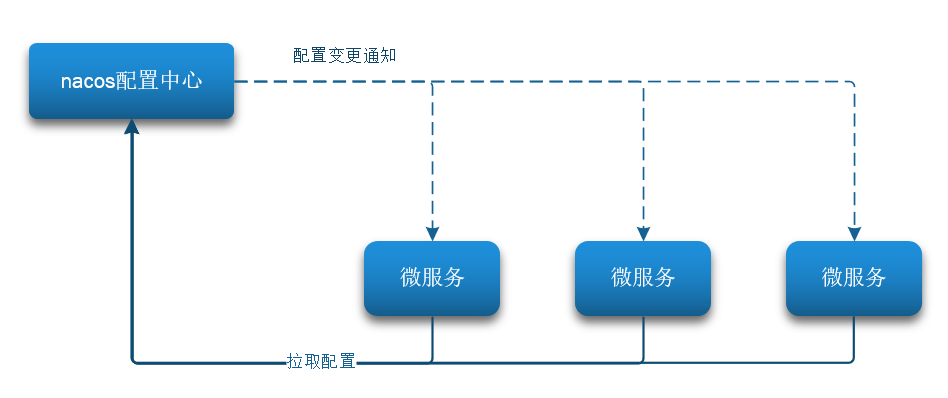
Nacos 一方面可以将配置集中管理,另一方可以在配置变更时,及时通知微服务,实现配置的热更新。
创建配置
在 Nacos 控制面板中添加配置文件

然后在弹出的表单中,填写配置信息:
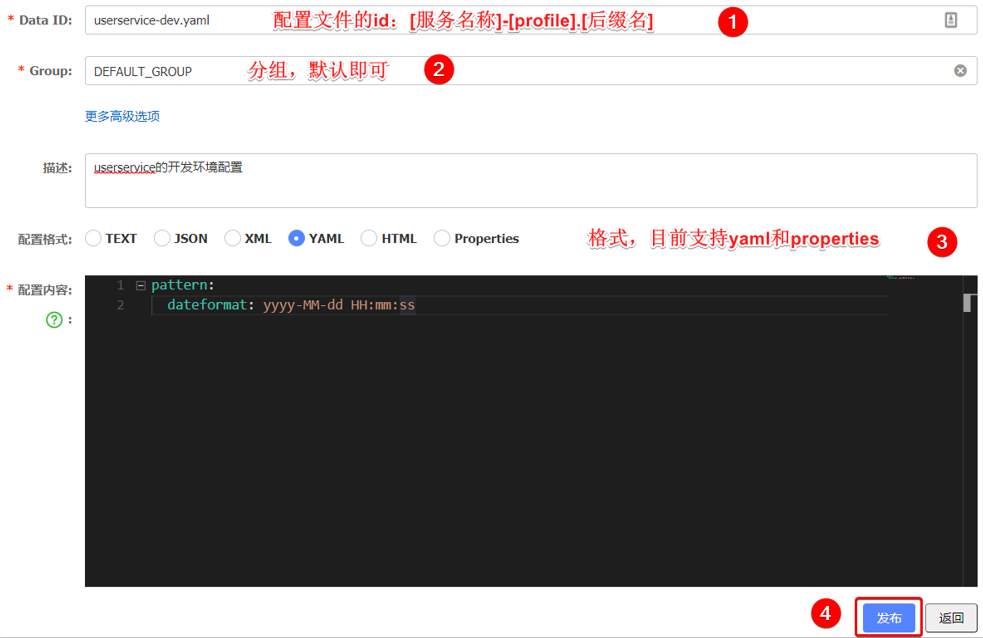
**注意:**项目的核心配置,需要热更新的配置才有放到 nacos 管理的必要。基本不会变更的一些配置例如数据库连接还是保存在微服务本地比较好。
拉取配置
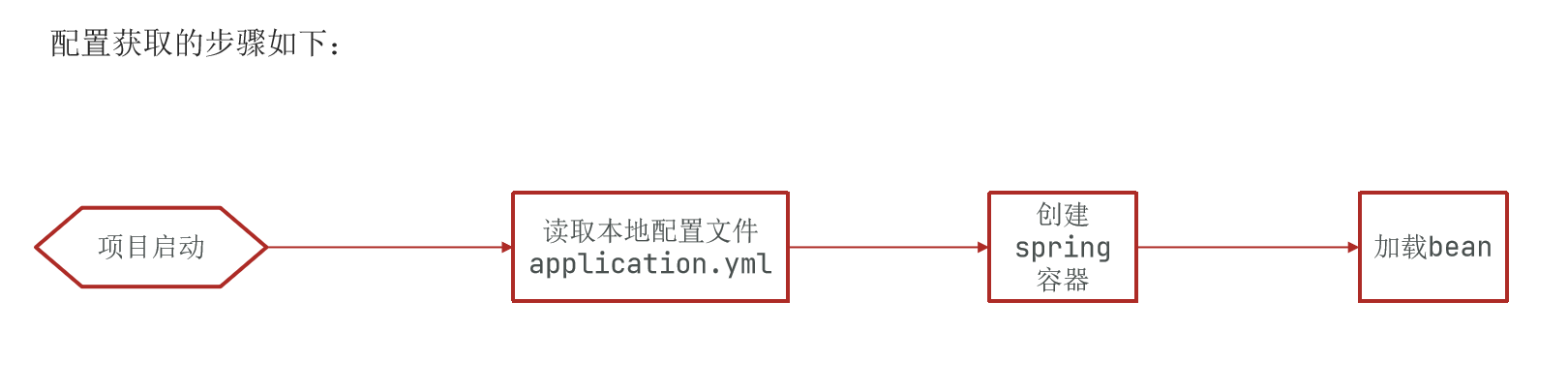
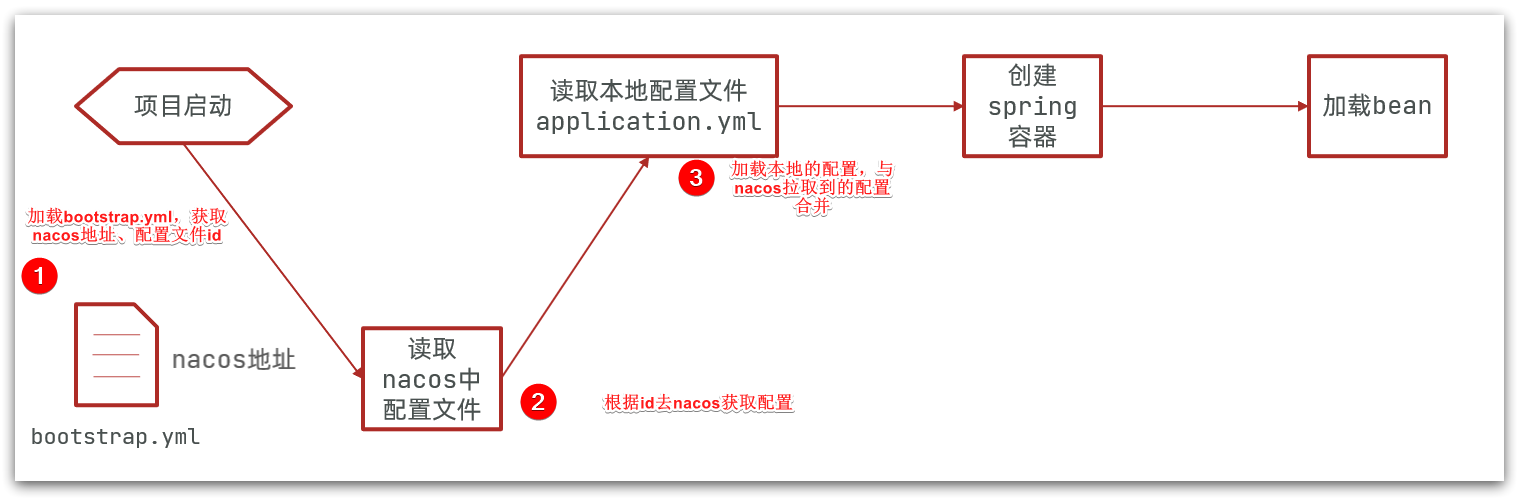
首先我们需要了解 Nacos 读取配置文件的环节是在哪一步,在没加入 Nacos 配置之前,获取配置是这样:
加入 Nacos 配置,它的读取是在 application.yml 之前的:
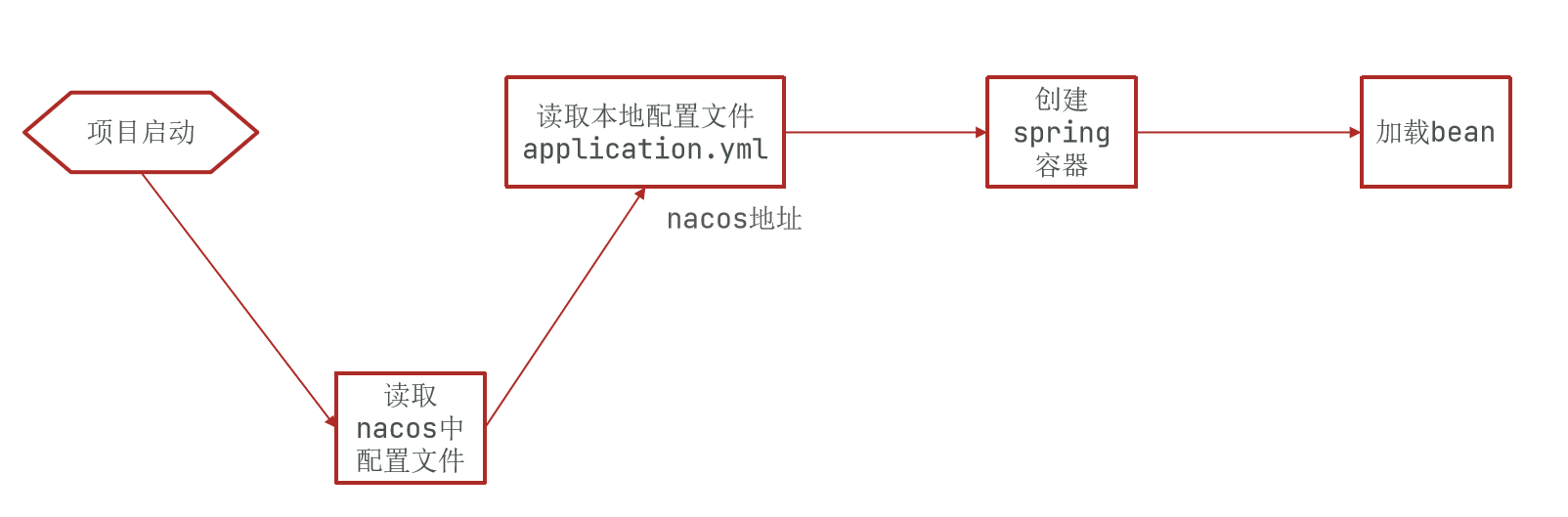
这时候如果把 nacos 地址放在 application.yml 中,显然是不合适的,Nacos 就无法根据地址去获取配置了。
因此,nacos 地址必须放在优先级最高的 bootstrap.yml 文件。
引入 nacos-config 依赖
首先,在 user-service 服务中,引入 nacos-config 的客户端依赖:
<!--nacos配置管理依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-config</artifactId>
</dependency>
添加 bootstrap.yml
然后,在 user-service 中添加一个 bootstrap.yml 文件,内容如下:
spring:
application:
name: userservice # 服务名称
profiles:
active: dev #开发环境,这里是dev
cloud:
nacos:
server-addr: localhost:8848 # Nacos地址
config:
file-extension: yaml # 文件后缀名
根据 spring.cloud.nacos.server-addr 获取 nacos地址,再根据${spring.application.name}-${spring.profiles.active}.${spring.cloud.nacos.config.file-extension}作为文件id,来读取配置。
在这个例子例中,就是去读取 userservice-dev.yaml

使用代码来验证是否拉取成功
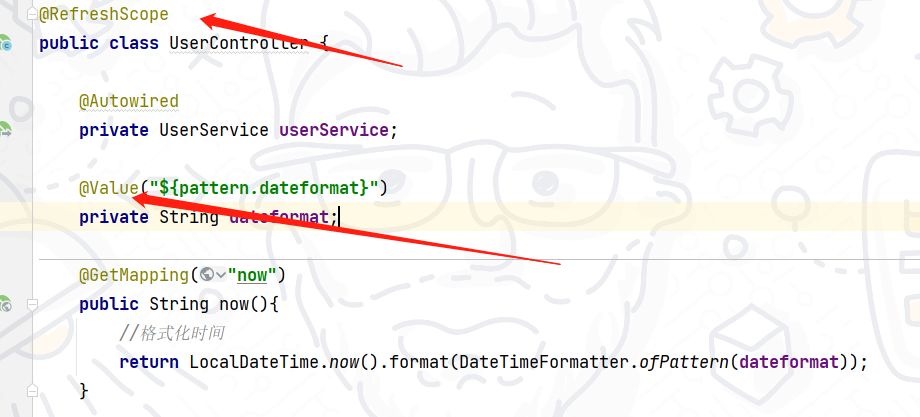
在 user-service 中的 UserController 中添加业务逻辑,读取 pattern.dateformat 配置并使用:
@Value("${pattern.dateformat}")
private String dateformat;
@GetMapping("now")
public String now(){
//格式化时间
return LocalDateTime.now().format(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern(dateformat));
}
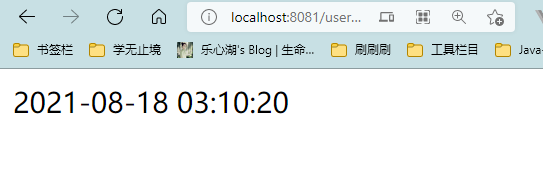
启动服务后,访问:http://localhost:8081/user/now
配置热更新
我们最终的目的,是修改 nacos 中的配置后,微服务中无需重启即可让配置生效,也就是配置热更新。
有两种方式:1. 用 @value 读取配置时,搭配 @RefreshScope;2. 直接用 @ConfigurationProperties 读取配置
@RefreshScope
方式一:在 @Value 注入的变量所在类上添加注解 @RefreshScope
@ConfigurationProperties
方式二:使用 @ConfigurationProperties 注解读取配置文件,就不需要加 @RefreshScope 注解。
在 user-service 服务中,添加一个 PatternProperties 类,读取 patterrn.dateformat 属性
@Data
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "pattern")
public class PatternProperties {
public String dateformat;
}
@Autowired
private PatternProperties patternProperties;
@GetMapping("now2")
public String now2(){
//格式化时间
return LocalDateTime.now().format(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern(patternProperties.dateformat));
}
配置共享
其实在服务启动时,nacos 会读取多个配置文件,例如:
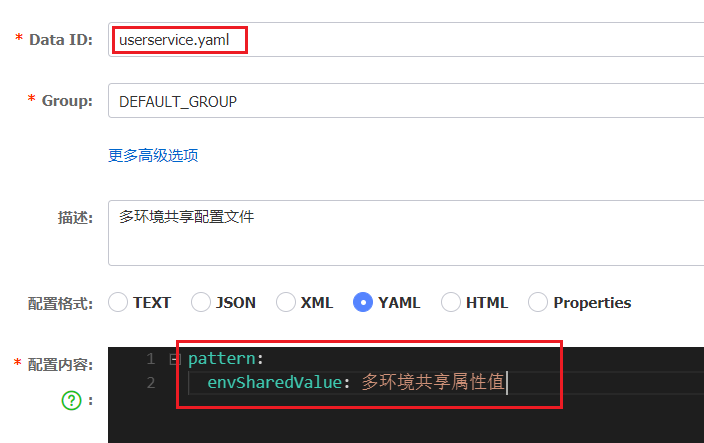
[spring.application.name]-[spring.profiles.active].yaml,例如:userservice-dev.yaml[spring.application.name].yaml,例如:userservice.yaml
这里的 [spring.application.name].yaml 不包含环境,因此可以被多个环境共享。
添加一个环境共享配置
我们在 nacos 中添加一个 userservice.yaml 文件:
在 user-service 中读取共享配置
在 user-service 服务中,修改 PatternProperties 类,读取新添加的属性:
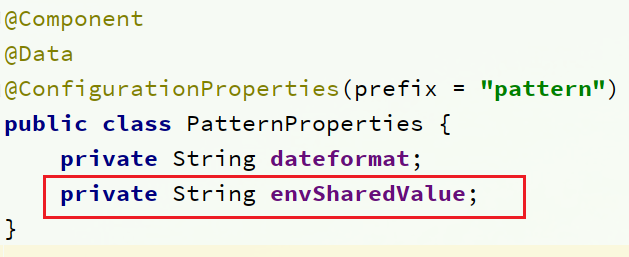
在 user-service 服务中,修改 UserController,添加一个方法:
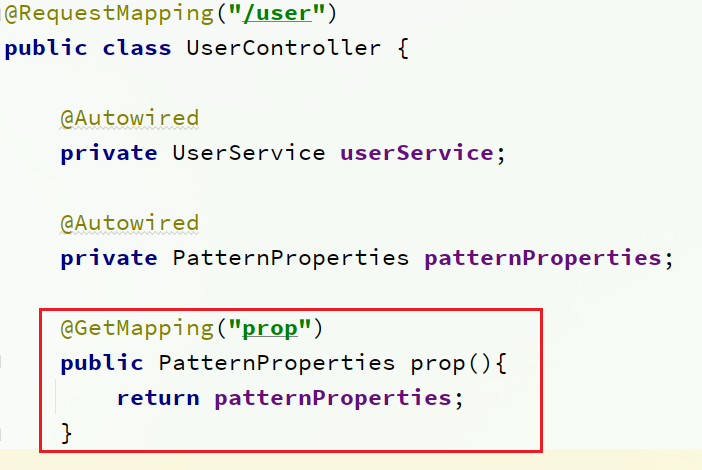
运行两个 UserApplication,使用不同的profile
修改 UserApplication2 这个启动项,改变其profile值:
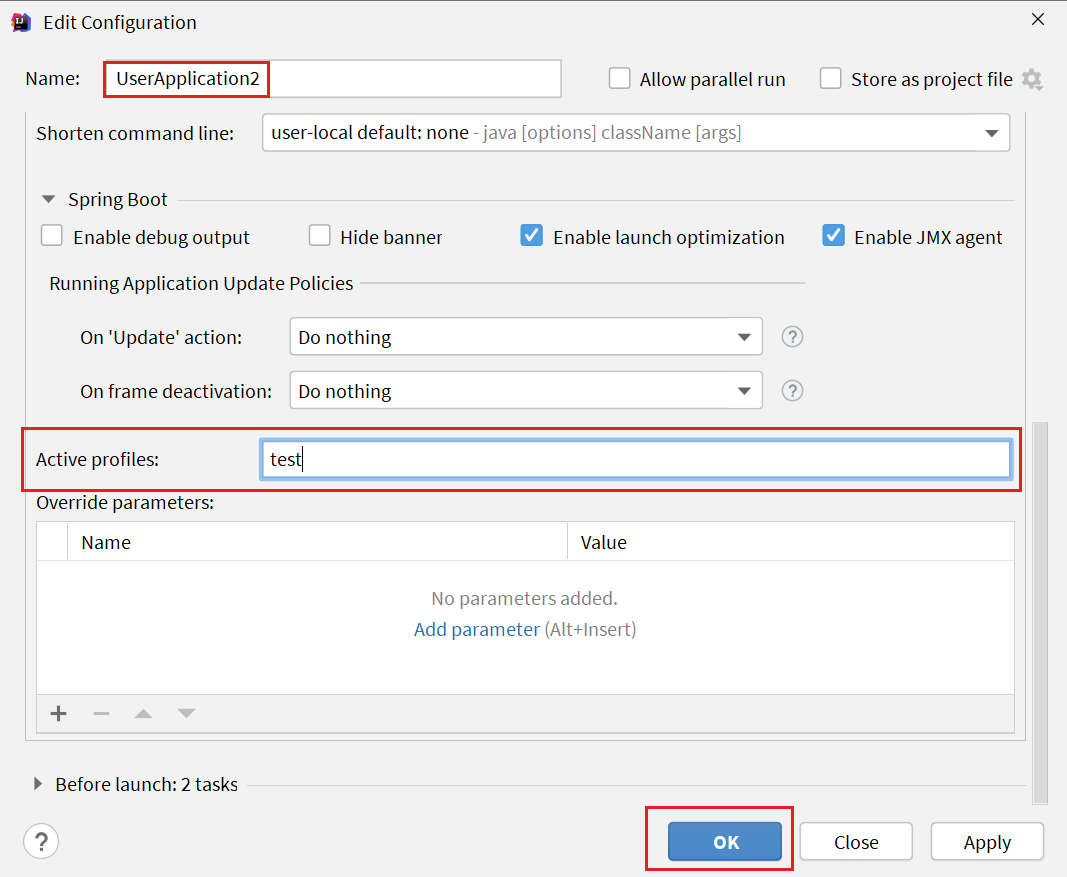
这样,UserApplication8081 使用的 profile 是 dev,UserApplication28082 使用的 profile 是test
启动 UserApplication 和 UserApplication2
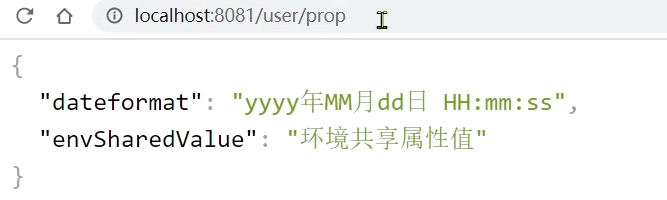
访问地址:http://localhost:8081/user/prop,结果:
访问地址:http://localhost:8082/user/prop,结果:

可以看出来,不管是 dev,还是 test 环境,都读取到了 envSharedValue 这个属性的值。
上面的都是同一个微服务下,那么不同微服务之间可以环境共享吗?
通过下面的两种方式来指定:
- extension-configs
- shared-configs
spring:
cloud:
nacos:
config:
file-extension: yaml # 文件后缀名
extension-configs: # 多微服务间共享的配置列表
- dataId: common.yaml # 要共享的配置文件id
spring:
cloud:
nacos:
config:
file-extension: yaml # 文件后缀名
shared-configs: # 多微服务间共享的配置列表
- dataId: common.yaml # 要共享的配置文件id
配置优先级
当 nacos、服务本地同时出现相同属性时,优先级有高低之分。

更细致的配置
